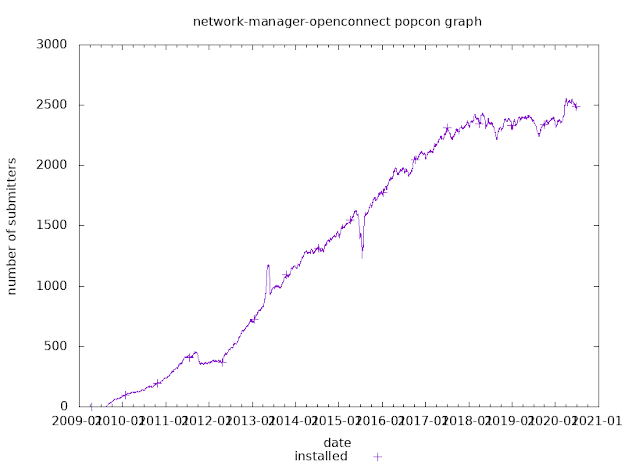
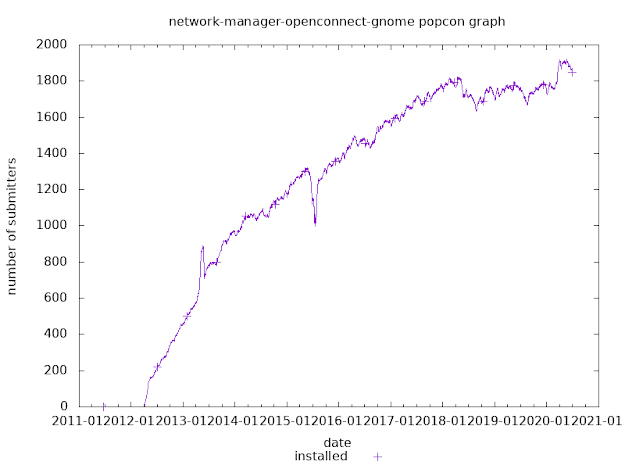
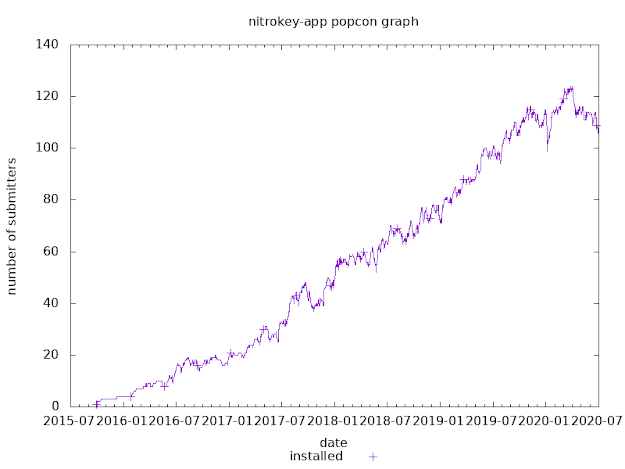
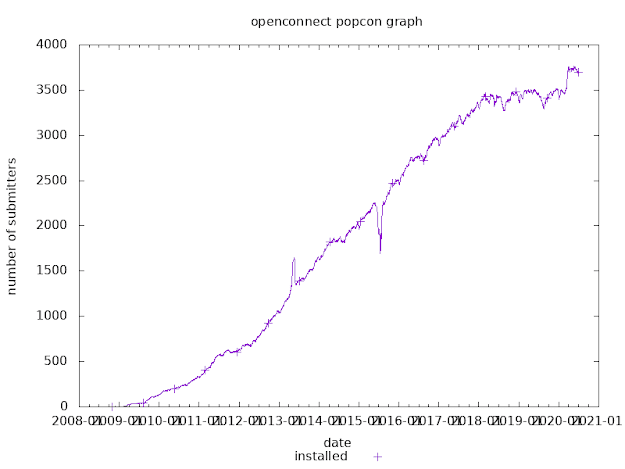
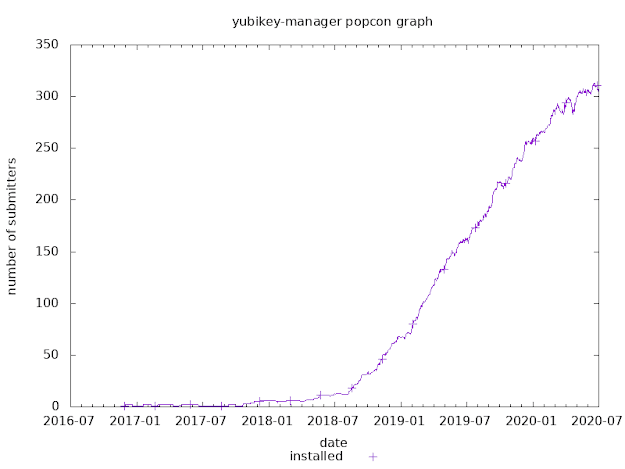
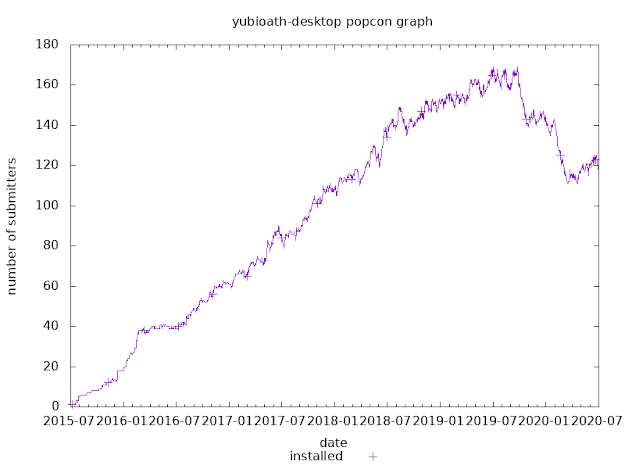
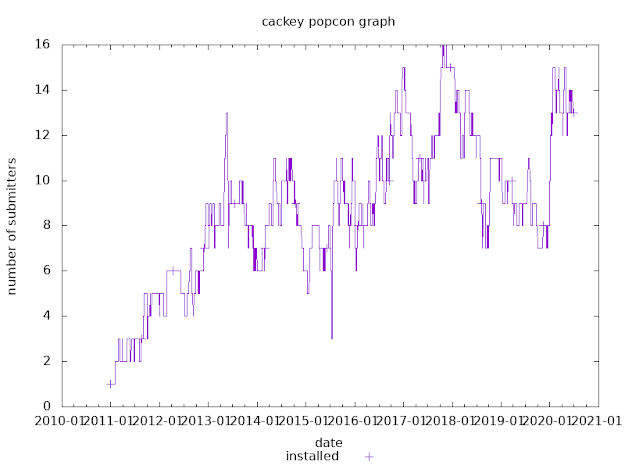
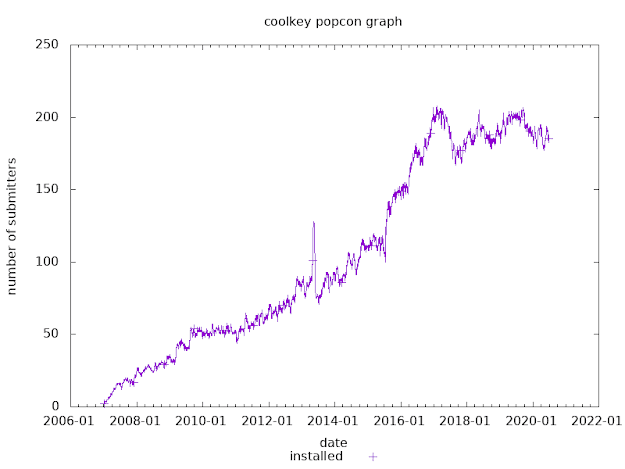
How to get smart card support
I, more and more, receive direct emails asking for help about a general question about smart cards.
Free support
It is OK to send me an email or create a github, salsa, etc. ticket if you find a bug in a
software I maintain. But it is, in general, not OK to contact me directly
because you have a problem with your smart card project.
I do provide Free Software (as in free speech), not free support (as in free beer). If you really want support from me then contact me, we can agree on something.
pcsclite-muscle mailing list
For community support you should use the pcsclite-muscle mailing list. You can
register to the list at
https://lists.infradead.org/mailman/listinfo/pcsclite-muscle
and access to the archives at
http://lists.infradead.org/pipermail/pcsclite-muscle/.
On the mailing list you will find many smart card experts. Some of them know much more about some smart card details than me. Most of the time I will answer your question. But some other people may have a better/different answer.
One major benefit of using a public mailing list is that you can find answers about already known problems in the mailing list archives. So the more users use the mailing list the richer the archives will be.
Mailing list success
Since 2009 I publish the mailing list statistics for the previous year. For example read "MUSCLE mailing list statistics for 2019".
The number of messages on the list is declining. In part because people use other ways to get answers: direct email to me, github issues, etc.
Conclusion
Email is an old technology. Mailing list is an old technology. You have to fight against spam, etc.
But I think it is a nice way to get free support.